In recent years, the automotive industry has witnessed a revolutionary shift toward autonomous driving technology. At the forefront of this evolution is the autopilot system, a groundbreaking innovation that empowers vehicles to navigate and operate without human intervention. One crucial component that makes autopilot systems possible is camera sensor detection. In this blog, we will delve into the fascinating world of autopilot and explore how camera sensors play a pivotal role in enabling vehicles to “see” and make informed decisions on the road.
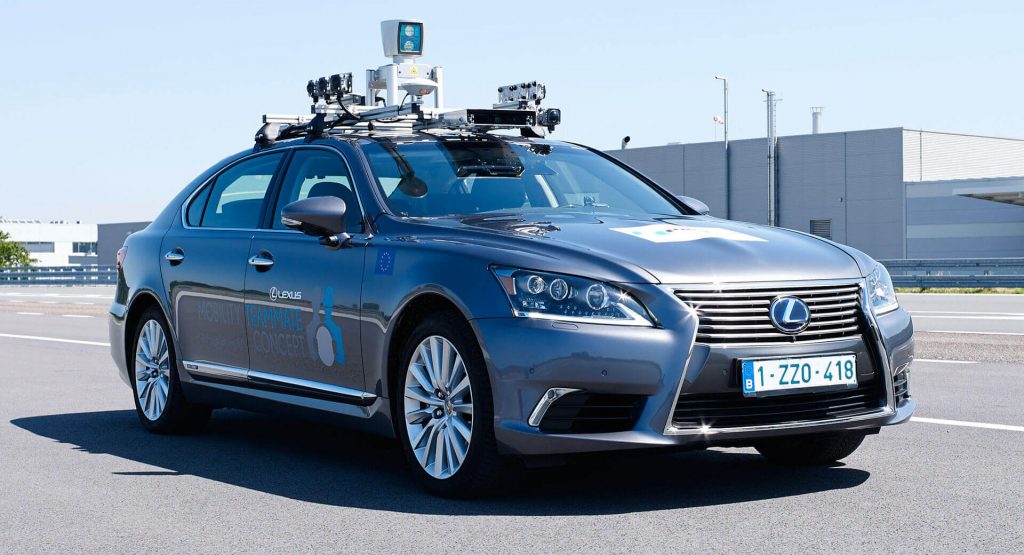

Autopilot, often associated with autonomous or self-driving vehicles, is a cutting-edge technology that combines various sensors, processors, and algorithms to replicate human driving capabilities. While autopilot may not entirely replace human drivers, it aims to enhance road safety, reduce accidents, and provide a more convenient driving experience. Among the multitude of sensors employed in autonomous driving systems, cameras stand out as a critical piece of the puzzle.
Camera sensors in autopilot systems mimic human visual perception by capturing the surrounding environment in real time. These high-resolution cameras are strategically positioned around the vehicle, offering a comprehensive view of the road, traffic, pedestrians, and obstacles. The cameras continuously gather data, feeding it into the vehicle’s central processing unit, which then employs sophisticated computer vision algorithms to interpret and make sense of the visual input.

Computer vision is the branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that equips machines with the ability to “see” and interpret visual information. In autonomous driving, computer vision algorithms analyze the camera data to recognize and classify objects, detect lane markings, identify traffic signs, and assess potential hazards. The AI algorithms can discern between different things, such as distinguishing between a car, bicycle, or pedestrian, and predict their movement to anticipate potential risks.
While camera sensors are incredibly versatile and effective, they do face particular challenges in autonomous driving scenarios. Adverse weather conditions like heavy rain, snow, or fog can hinder visibility and affect the camera’s ability to detect objects accurately. However, modern camera sensor technology incorporates advanced features like infrared imaging and thermal sensors to mitigate these challenges.
Another challenge involves handling complex and dynamic driving environments, such as bustling city streets or highways with multiple lanes and fast-changing traffic patterns. To address this, autonomous vehicles rely on a combination of sensor inputs, including LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and RADAR (Radio Detection and Ranging), to complement the camera data and create a comprehensive 360-degree view of the surroundings.
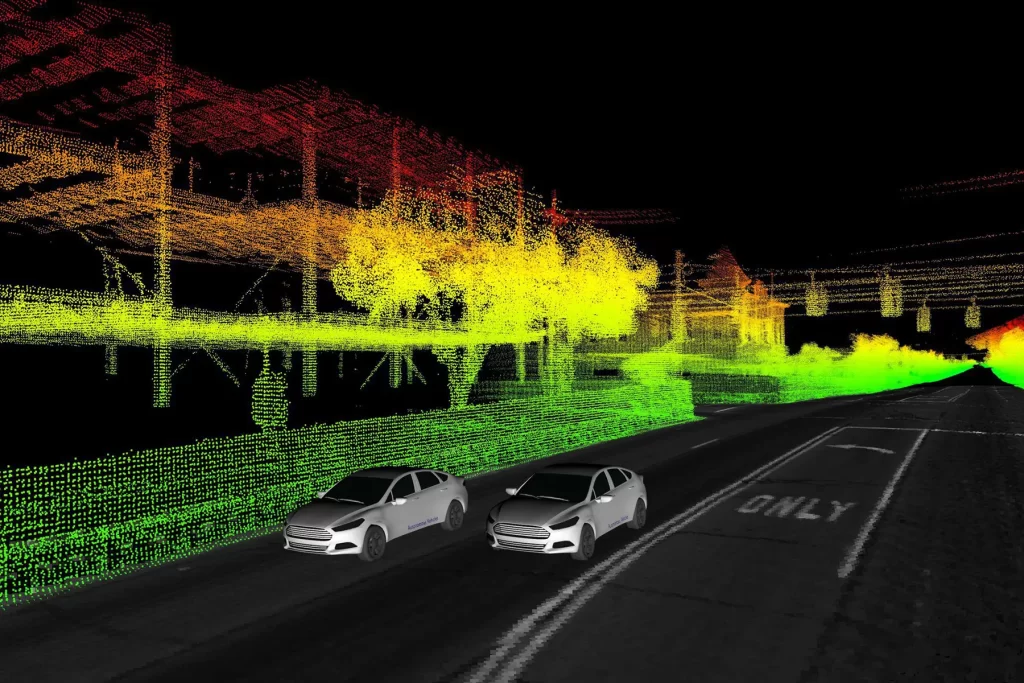

The success of autonomous driving systems heavily depends on the ability to learn from real-world experiences and improve over time. Camera sensors play a crucial role in this aspect, as they enable data collection from countless driving scenarios, contributing to a vast dataset. This data is fed back into the AI algorithms, facilitating continuous learning and enhancing the system’s decision-making capabilities.
Safety is paramount in the realm of autonomous driving. To ensure redundancy and backup, autonomous vehicles often integrate multiple camera sensors. These redundant cameras act as backups, enabling the system to maintain functionality even if one or more cameras fail or experience temporary issues.
The evolution of autopilot technology with camera sensor detection has brought forth a new era of mobility. The combination of camera sensors and advanced AI algorithms empowers vehicles to “see” the world around them, make real-time decisions, and navigate safely through complex driving environments. While the journey towards fully autonomous driving is ongoing, the continuous advancements in camera sensor technology, computer vision, and AI algorithms pave the way for a future where self-driving vehicles become a common sight on our roads, revolutionizing transportation and enhancing road safety for all.


